Building the immune system as a daily routine is important to the health of individuals. We should fight the urges for substances that compromise our systems and chemicals in foods that break down our immunity and open doors to infectious diseases.
Water, fresh vegetables, and more fruits can help in the fight for a stronger immune system. Too many sugars and processed foods will make it harder to fight against infections.
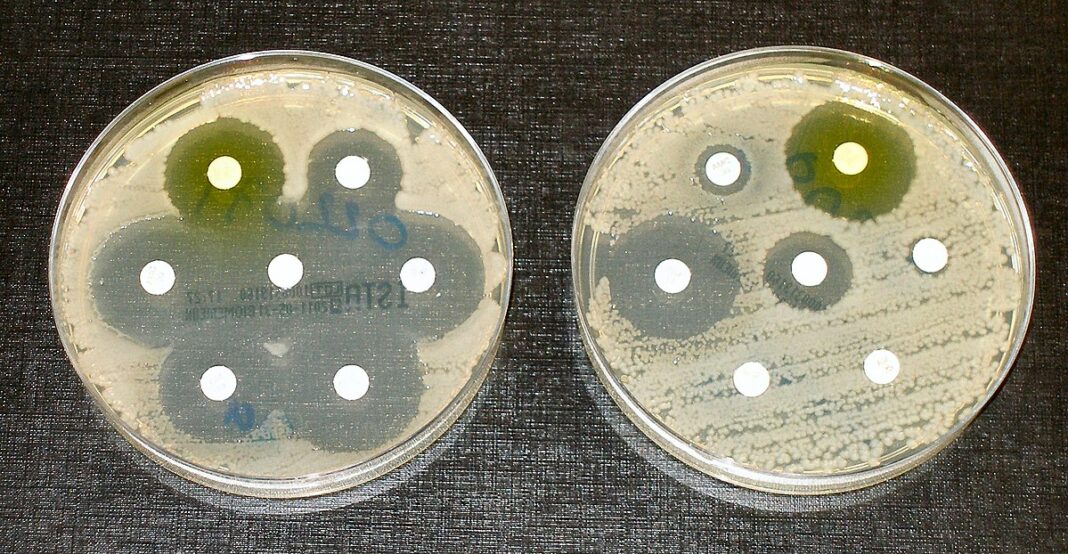
In a recent report, “Despite more than a century of antibiotic research and development, the world is quickly running out of these lifesaving drugs.
Antibiotics, either found in nature or developed intentionally, are designed to kill bacteria. But bacteria have been evolving for more than 3 billion years and have learned to change themselves to survive. The more we use them, the more they adapt.
In 2019, the last year data is available, more than 2.8 million Americans had antimicrobial-resistant infections and more than 35,000 died, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Worldwide, deaths already top 5 million a year and are expected to grow into the tens of millions within a few decades.
“We are truly right now in the midst of this crisis,” Brenda Wilson, a Professor of Microbiology at the University of Illinois said in a recent American Society for Microbiology talk.
The U.S. was making solid progress against antibiotic resistance before the pandemic. Thanks to improved infection prevention and control and better stewardship, deaths from antimicrobial resistance declined by 18% overall and 30% in hospitals from 2012 to 2017.
But the pandemic pushed hospitals and other health care facilities near their breaking point in 2020, leading to an increase in antibiotic use, trouble following infection prevention and a significant increase in resistant infections in U.S. hospitals, the CDC found. Resistant hospital-onset infections and deaths both increased at least 15% that year, although data outside hospitals is lacking.
Overuse, both among people who would have recovered without the drugs and in livestock who get them to promote growth not treat illness, helps drive resistance.
And there’s a tremendous human cost, in addition to the financial one.
“A lot of what we do in medicine relies on our ability to handle bacterial infections that occur along the way,” said William Hanage, who co-directs the Center for Communicable Disease Dynamics at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Minor injuries can become life-threatening without antibiotics.
Many surgeries wouldn’t be able to happen without knowing there were antibiotics to prevent any later infections.
Patients need antibiotics if they’re being treated with steroids or for cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, or other conditions that limit their immune response, as do people like Lawrence, who has cystic fibrosis, which makes her vulnerable to every passing bug.
“We want to be able to handle these things,” Hanage said.
“The market is broken because it’s focused on volume. Antibiotics should not be used in high volume,” said Dr. Helen Boucher, dean of the Tufts University School of Medicine.
She and others are encouraging Congress to pass a bill called the Pioneering Antimicrobial Subscriptions To End Up surging Resistance (or PASTEUR) Act, named for Louis Pasteur, the 19th-century Frenchman often considered the “father” of germ theory and modern microbiology. The bill was first introduced in 2020.
It would create new incentives for drug companies to discover and develop antibiotics.
Food supply
The commercial raising of animals for food has contributed to the problem. For decades, breeders have fed their livestock antibiotics. At first, they started out trying to help sick animals get well. But they noticed that animals fed antibiotics got big faster. So it became standard practice to include antibiotics in the feed of every animal, from poultry to fish to pigs to cows.
“The nature of raising animals in the backyard or a big barn really motivates the spread of microbes and facilitates the spread,” Johnson said. “Those microbes have the potential to enter humans.”
In recent years, under pressure from advocates, some companies have promised to cut back on the routine feeding of antibiotics. But some of those promises ring hollow, advocates say, or have been hard to maintain in a competitive marketplace.
Earlier this month, Tyson Foods, the largest chicken producer in the United States, moved away from the “no antibiotics ever” pledge it made in 2015. Instead, the company is transitioning to “no antibiotics important to human medicine” by the end of this year. It uses essential oils and botanicals like oregano and thyme, as well as probiotics as antibiotic alternatives, and says it is “making significant progress eliminating the use of antibiotics also important to human health from our chicken production.”
While most farms don’t use “medically important” antibiotics, using disinfectants or other methods to prevent certain types of bacteria from taking hold can inadvertently favor other potentially dangerous bacteria, Johnson said.
When bacteria develop drug-resistant genes, he said they can jump from one pathogen to another. This tends to occur in microbiomes, like the gut, which are rich in microorganisms and motivate the drug-resistant gene to spread between bacteria to survive.
Drug-resistant genes can also hop from non-threatening bacteria found in animals to pathogens that are more harmful to humans.
“Those resistances don’t tend to go away easily,” Johnson said…READ MORE
DISCLAIMER: The content of Pro Liberation is firmly opinionated and is not meant to be interpreted as official news. We glean facts and quotes from mainstream news websites and abridge its meaning for readers to relate. We do not indulge in misinformation, conspiracy theories, or false doctrine but choose to express our right to free speech as citizens of this country and free born under God the Creator. We represent Nu Life Alliance Inc. a non-profit organization in the battle for social and economic justice. Donate to our cause at the following link. DONATE